Medicines are products that contain active ingredients. An active ingredient is a chemical compound that can be used to cure, halt or prevent disease; ease symptoms; or help in the diagnosis of illness. Active ingredients may be based on molecules extracted from plants, made by a chemical reaction in a laboratory, or be the byproduct of organisms such as fungi.
Medicines may be in the form of liquids, tablets, capsules, inhalers, creams, drops and patches.
Medicines act in a variety of ways.
Antibiotics can cure an illness by killing or halting the spread of invading bacteria.
Some medicines can control problems such as high blood pressure.
Medicines like insulin can replace missing substances or corrects low levels of natural body chemicals.
Analgesics are medicines which block the pathways that transmit pain signals from the injured or irritated body part to the brain, relieving pain.
Vaccines can protect the body against some infectious diseases. They teach your body to make the correct antibodies to fight against the disease if you catch it.
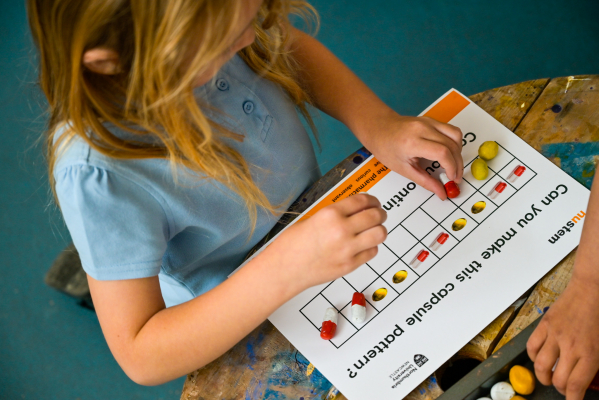
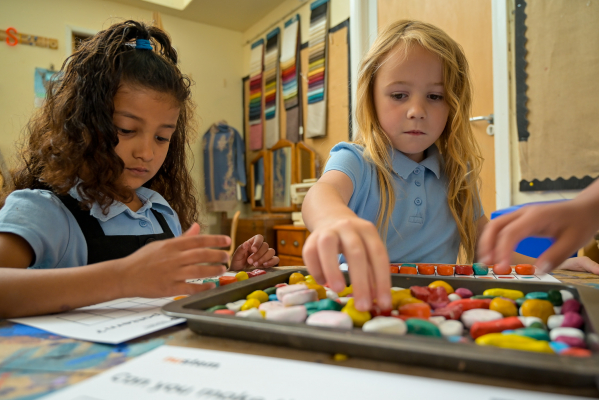
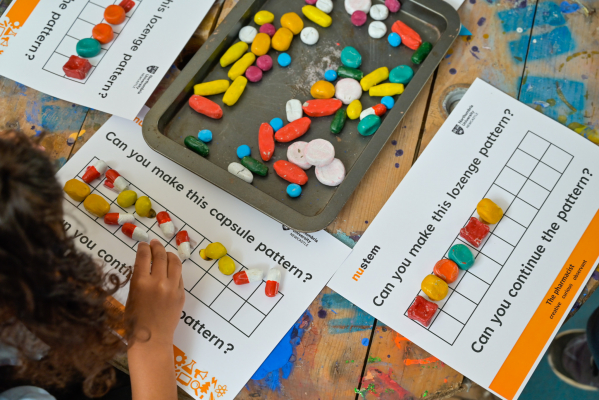
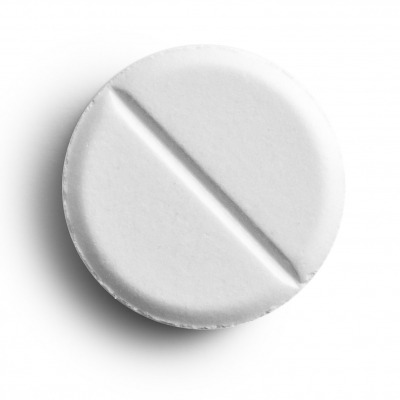




 A tablet is a hard and compressed medication in a round, oval, or square shape. The active ingredient is combined other substances to make the tablet sturdy enough to be packaged and transported. Some tablets have a coating to protect against stomach acids and delay the release of the drug into the blood stream. These tablets should not be crushed or chewed. Some tablets are soluble and are designed to be dissolved in water. The active ingredient in the tablets are eventually absorbed into your bloodstream and travel around your body.
A tablet is a hard and compressed medication in a round, oval, or square shape. The active ingredient is combined other substances to make the tablet sturdy enough to be packaged and transported. Some tablets have a coating to protect against stomach acids and delay the release of the drug into the blood stream. These tablets should not be crushed or chewed. Some tablets are soluble and are designed to be dissolved in water. The active ingredient in the tablets are eventually absorbed into your bloodstream and travel around your body. In a capsule the active ingredient is contained inside a plastic shell that dissolves slowly in the stomach. Some capsules need to be swallowed whole but others can be split open and the contents mixed with food or liquid. Capsules with a hard shell have two halves which fit inside each other to form a closed casing. They can be filled with dry or liquid ingredients, and can contain more than one active ingredient. Some capsules have a soft-gel coating, and may be semi-transparent. They contain medication suspended in gelatin (or similar substance) that is easily digested so the active ingredients are released and absorbed quickly.
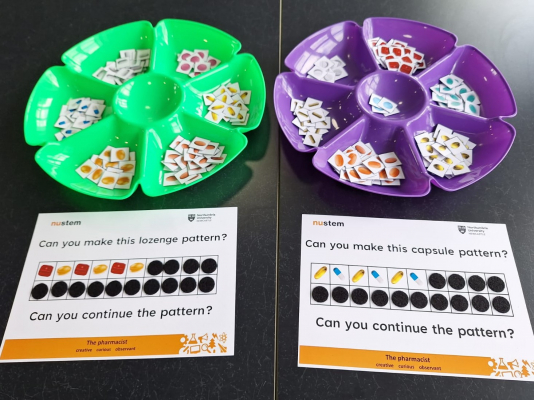
In a capsule the active ingredient is contained inside a plastic shell that dissolves slowly in the stomach. Some capsules need to be swallowed whole but others can be split open and the contents mixed with food or liquid. Capsules with a hard shell have two halves which fit inside each other to form a closed casing. They can be filled with dry or liquid ingredients, and can contain more than one active ingredient. Some capsules have a soft-gel coating, and may be semi-transparent. They contain medication suspended in gelatin (or similar substance) that is easily digested so the active ingredients are released and absorbed quickly.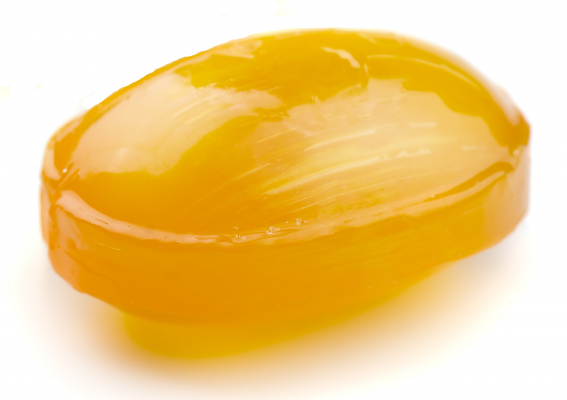 Lozenges are solid pills which are designed to dissolve slowly in the mouth. They are often flavoured and sweetened so they taste nice. They release their active ingredients slowly. Lozenges may contain anaesthetics, antiseptics or something to soothe the throat (a demulcent). They are generally used to treat mouth or throat illnesses.
Lozenges are solid pills which are designed to dissolve slowly in the mouth. They are often flavoured and sweetened so they taste nice. They release their active ingredients slowly. Lozenges may contain anaesthetics, antiseptics or something to soothe the throat (a demulcent). They are generally used to treat mouth or throat illnesses.