Play, Be, C: The Magnet Engineer
Resources and activities themed around a STEM job, to build language and understanding around the world of work.
Resources and activities themed around a STEM job, to build language and understanding around the world of work.
Magnetic engineers design magnets, or machines and devices that contain magnets. Magnets are in many of the systems that make modern life possible. For example they are used in computer data storage, alarm systems, microphones and speakers, motors, electrical generators and transformers.
Magnet engineers are:
Curious about how they can use magnets in different machines.
Creative when they use magnets in their designs.
Observant as they look closely at what magnets can do.
Includes statements from Development Matters (birth to age five) and the relevant ELGs.
Play, Be, C Units provide enabling environments with teaching and support from adults. Reflecting on the characteristics of effective teaching and learning, children will have opportunity to learn and develop by:
- Playing and exploring – children investigate and experience things, and ‘have a go’.
- Active learning – children concentrate and keep on trying if they encounter difficulties and enjoy achievements.
- Creating and thinking critically – children have and develop their own ideas, make links between ideas, and develop strategies for doing things.
Early Years Foundation Stage Statutory Framework: accessed November 2024. Available under the Open Government Licence v3.0.

Our suggested book for this Unit is No-Bot the Robot with No Bottom by Sue Hendra, illustrated by Paul Linnet.
You can find out more about the book at the publisher’s page, and the Google Books page will link you to retailers and local libraries.
We have designed these STEM-focused questions to use alongside the questioning you would usually use when reading a story.
These adult led activities and provocations will support the introduction of the robotics engineer career to the children in your setting.
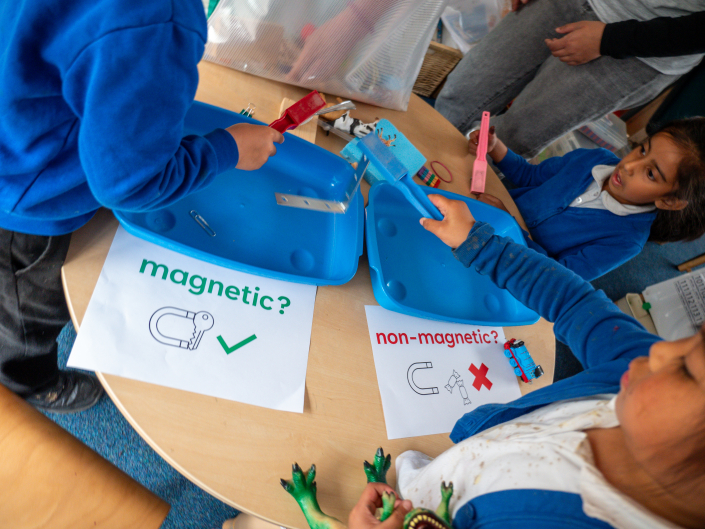
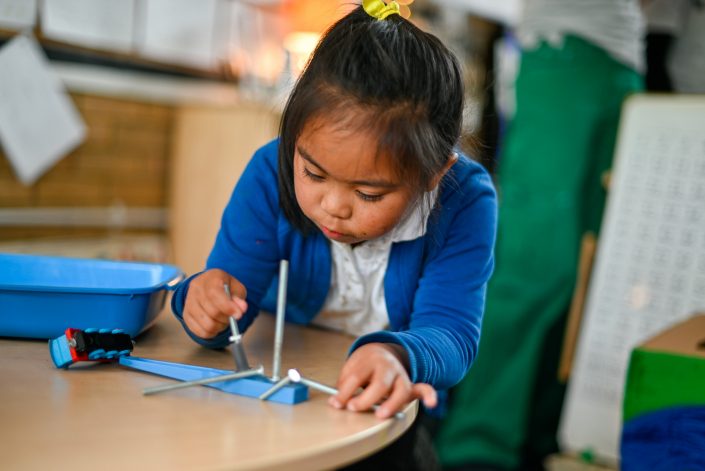
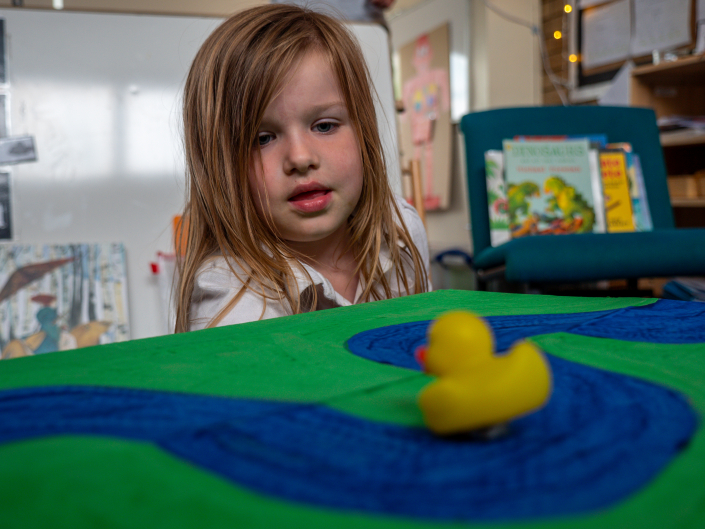






We have included these links to our related STEM at home activities. These could be sent out for families to try at home, or run in school at a family session.
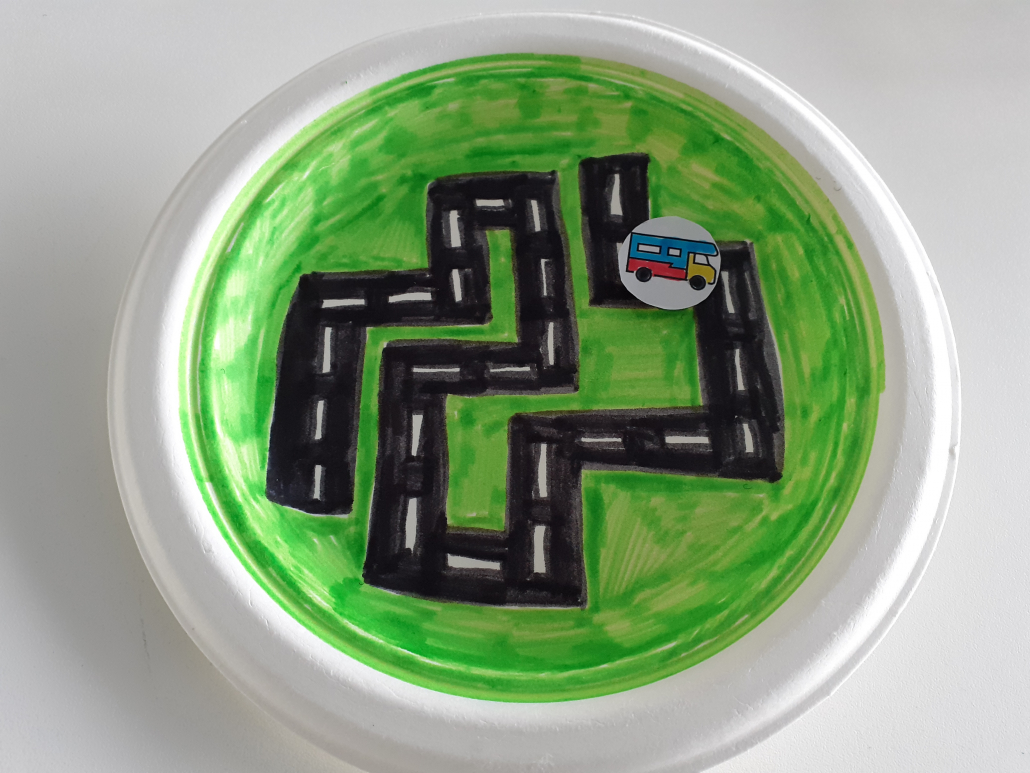

This is a link to the instructions for a related family STEM story time activity. This is an opportunity to introduce STEM ideas and activities to parents, carers and other family members in a relaxed and enjoyable way.
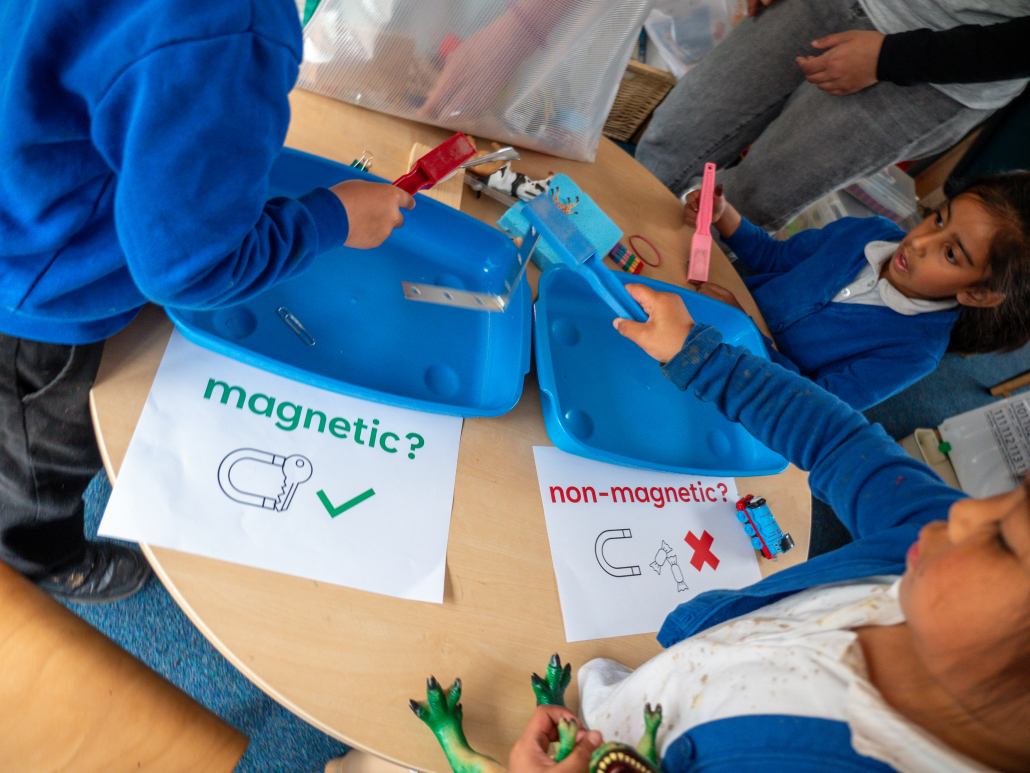

 Magnetic engineers design magnets, or machines and devices that contain magnets. Magnets are in many of the systems that make modern life possible. For example they are used in computer data storage, alarm systems, microphones and speakers, motors, electrical generators and transformers.
Magnetic engineers design magnets, or machines and devices that contain magnets. Magnets are in many of the systems that make modern life possible. For example they are used in computer data storage, alarm systems, microphones and speakers, motors, electrical generators and transformers.
Electricity generation relies on magnets to create and electric current, and magnets are used in transformers in the National Grid to transfer the electricity around the country. Some vending machines use magnets to differentiate coins from other material to prevent theft.
Large electromagnets are used in construction and at junkyards to move materials. They are also used to suspend and accelerate maglev trains.
Magnets are also used in MRI scanners in hospitals which helps to produce detailed three dimensional images of inside the body.
After a magnet has been designed, magnet engineers define manufacturing processes and testing strategies, then analyse test results, and present them in the form of operating instructions and manuals.
You can download our magnet engineer poster to use in your setting.
We may request cookies to be set on your device. We use cookies to let us know when you visit our websites, how you interact with us, to enrich your user experience, and to customize your relationship with our website.
Click on the different category headings to find out more. You can also change some of your preferences. Note that blocking some types of cookies may impact your experience on our websites and the services we are able to offer.
These cookies are strictly necessary to provide you with services available through our website and to use some of its features.
Because these cookies are strictly necessary to deliver the website, refusing them will have impact how our site functions. You always can block or delete cookies by changing your browser settings and force blocking all cookies on this website. But this will always prompt you to accept/refuse cookies when revisiting our site.
We fully respect if you want to refuse cookies but to avoid asking you again and again kindly allow us to store a cookie for that. You are free to opt out any time or opt in for other cookies to get a better experience. If you refuse cookies we will remove all set cookies in our domain.
We provide you with a list of stored cookies on your computer in our domain so you can check what we stored. Due to security reasons we are not able to show or modify cookies from other domains. You can check these in your browser security settings.
These cookies collect information that is used either in aggregate form to help us understand how our website is being used or how effective our marketing campaigns are, or to help us customize our website and application for you in order to enhance your experience.
If you do not want that we track your visit to our site you can disable tracking in your browser here:
We also use different external services like Google Webfonts, Google Maps, and external Video providers. Since these providers may collect personal data like your IP address we allow you to block them here. Please be aware that this might heavily reduce the functionality and appearance of our site. Changes will take effect once you reload the page.
Google Webfont Settings:
Google Map Settings:
Google reCaptcha Settings:
Vimeo and Youtube video embeds:
The following cookies are also needed - You can choose if you want to allow them:
You can read about our cookies and privacy settings in detail on our Privacy Policy Page.
Privacy Notice and Cookies 2025